Aerial Roof Moisture Survey
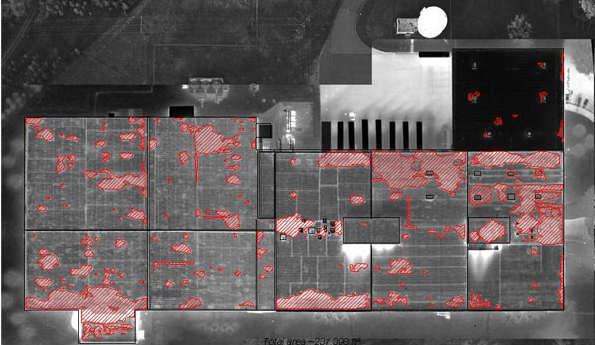
Aerial roof moisture surveys provide a more comprehensive and accurate way to detect roof moisture issues. This infrared roof scan method provides more useful data to decision makers than walk-on surveys are able to provide.
Advantages of Aerial Infrared Roof Scanning
The biggest advantage of an aerial infrared roof survey comes from the ease of quickly and easily scanning roofs. It can be difficult, costly, dangerous, or even impossible to survey roofs using an “on-ground” technique. Aerial surveys are typically more cost effective, quicker, and easier than “on-ground” surveys.
With high-resolution plan view aerial imagery, we can see slight temperature nuances from a distance. This allows us to identify the pattern of heat and pinpoint the exact location of issues.
Fixed-Wing ‘Plan View’ Aerial Infrared
- High-resolution images capture large areas at once, making report writing easier and less expensive to produce.
- Plan view allows for infrared images, visual images and AutoCAD drawings to be reconciled closely. As a result, the report is clear, concise and easy to understand.
- Plan view imaging allows accurate marking of areas of suspect roof moisture contamination.
- The printed AutoCAD drawings can be used on the roof to paint areas of moisture contamination directly on the roof (after verification), if desired.
- The trending of roof moisture becomes possible.
Buy only the report you need
- Further processing can be done on roof areas of specific concern. The report components are as follows in order by cost:
- Unedited videotape: The raw videotape of the infrared flight over the building.
- Edited videotape: An edited videotape can be made from the original digital video.
- Printed thermographs: Printed infrared thermographs of each roof section can be captured and printed in high-resolution.
- Aerial photographs: Printed digital and/or conventional photographs of the roof (straight down) and site (beauty shots of the building and property) can be printed. Note: A straight down photograph of a roof section aids significantly in the infrared analysis, showing stains, equipment and roof boundaries, etc.
- AutoCAD drawings: Accurate AutoCAD drawings can be made, then printed and saved to a disk
- Digital and printed report: A complete quantitative aerial infrared roof moisture survey report would include all of the above, printed in high resolution and saved to a CD.
Roof Analysis Using Infrared Technology
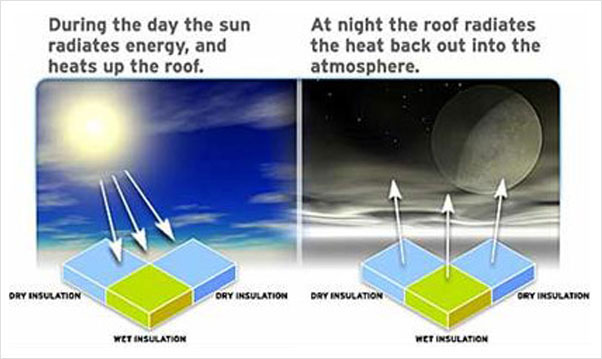
Heat Retention
During the day, the sun radiates energy onto the roof and into the roof substrate. At night, the roof radiates the heat back into outer space through radiational cooling. Infrared imagers can detect this heat, identifying the warmer, higher mass areas of the roof, during the “window” of uneven heat dissipation.
Survey Conditions
For optimal survey results, we recommend conducting the survey on a dry roof with low wind conditions and in the absence of precipitation. Aerial infrared technology allows for recognition of slight temperature nuances over large areas. A high angle of view and high resolution are necessary to produce usable imagery.
Equipment and Data Collection
We use state-of-the-art, large-format infrared cameras with at least 512 x 512 staring array detectors (262,144 pixels). From an altitude of 1,200 – 1,500 feet above the roof with over a quarter of a million pixels, the ground resolution element is about six inches square. Visual photographs are taken earlier in the day or the next day.
Analysis and Reporting
We use both visual and infrared images to analyze by overlaying the AutoCAD drawing of the roof ‘over’ the digitized photographs and thermographs. We create drawings that indicate areas of suspected moisture contamination. Our reports integrate visual, infrared and AutoCAD components (printed and video) that we match and align well.
General Roof Maintenance
Manifestation of Problems
Waterproofing issues display in two forms: leakage and entrained moisture contamination. Locating leaks can be difficult as water often flows down the slope of the roof to a spot that is not sealed and enters into the building from there. Leaks mostly happen at the sealed areas of waterproofing or where there is a penetration of the roof. Finding the exact spot of water contamination in the insulation can be difficult.
Surveys for Water Detection
We use three types of surveys to find water issues in a roof: Nuclear gauges (count neutrons), capacitance meters (measure resistance), and infrared (measures heat). Nuclear gauges and capacitance meters take spot readings on a 5’ X 5’, 10′ X 10′ or 20′ X 20′ grid on the roof to determine the origin of water. These types of surveys are costly and labor-intensive, typically used for roofs that do not gain or lose much solar energy, and don’t lend themselves to infrared.